
Rubber Moulding Techniques
June 06, 2023 · Neethu A S
Moulding is the operation of shaping and vulcanising the plastic- rubber compounds by means of heat and pressure, in a mould of appropriate form. Fundamentally, all the processes of moulding are similar, the way of introducing the material in to the mould distinguish one technique from another. The basic process is
- Injection moulding
- Transfer moulding
- Compression moulding
INJECTION MOULDING
Rubber injection moulding is very similar to the more well-known plastic injection moulding process. It starts with the uncured rubber strips that go into the machine via a hopper. Once through the hopper, it enters the screw chamber, where it is heated and near the end of the screw, the rubber has heated to a very fluidic state. It is fed into the mould at high pressure and it fills up the cavity built inside the rubber mould. Due to its flow properties, the rubber material fills every nook and cranny of the cavity.
The mould then gradually cools down so the rubber solidifies. Finally, the mould opens to eject the end product, after which it is ready for the next cycle
.png)
ADVANTAGES OF INJECTION MOULDING
High Accuracy: The application of pressurized rubber injection along with the good flow properties of rubber allows the raw material to fully fill up the mould and reach every corner. The result is thus very precise.
Complex Geometry: This method can manufacture designs with special features like holes, curvature, and sharp contours. The mould cavity design has a lot of flexibility and it can accommodate elements like cores to allow for complex features in the rubber part.
High Mechanical Strength: Due to pressure and ample curing time, the parts have high strength and durability.
No Finishing: Injection moulded rubber products have fewer defects or leftover material that needs after it comes out from the mould. Except for a small parting line and gate vestige, the output is a near-net shape.
Quick Process: Modern control technologies ensure precise control of heat and pressure in injection moulding machines. Optimization of these processes can lead to short curing cycles, giving a major advantage in terms of time.
Economies of Scale: Apart from initial tooling costs, the moulding cost per item is quite low. If mass production is the goal, it is perhaps the best way to maximize profitability.
DISADVANTGES of Rubber Injection Moulding
Material Limitations: One downside to rubber injection moulding is that it requires good flow properties. Not all rubbers have the necessary properties so the raw material options are limited to flexible, liquid-like rubbers like silicone rubber, polyurethane, nitrile rubber, etc. However, most rubber materials are capable of injection moulding.
High Initial Costs: The tooling cost and the moulding machine are expensive. Hence, it is sometimes not financially viable for low volume injection moulding./p>
Rubber Transfer Moulding
Transfer moulding utilizes a distinct rubber mould design. The die mould has two halves like any other mould but the upper half has an additional open-ended cavity known as the pot. A spruce network connects the pot and the main cavity. The preform is placed into this pot and ‘transferred’ into the cavity by a plunger through high pressure and heat.
The raw material then cures and solidifies. Finally, the mould ejects the final product once it has cooled down and vulcanized.
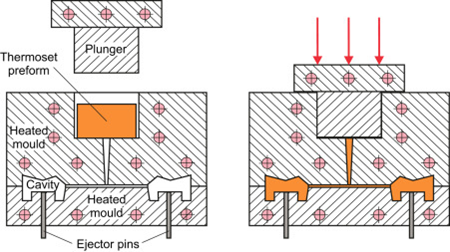
Advantages of transfer moulding
Tight Tolerance: This technique can provide rubber moulded parts with dimensional tolerance and is very suitable manufacture accurate part geometries.
Metal Bonding: Rubber-to-metal bonding is a strong point of transfer moulding. It is a convenient method to manufacture parts like combined metal-rubber mounts.
Large Parts: The mould design can include large cavities with ease.
High Cavity Count: The pre-form is a very simple shape and does not require much preparation. As a result, the same preform is reusable for many cycles without much hassle, saving time and effort.
Disadvantages of transfer moulding
High Tooling Cost: The mould has additional features like the pot and spruce. These make it more complex to design and manufacture. But the complexity also adds cost to the initial setup.
Finishing: Deflashing is always necessary when using transfer moulding due to the spruce.
High Cycle Time: Unlike other processes, the curing time is high for this technique, which is an important consideration in many processes
RUBBER COMPRESSION MOULDING
Compression moulding, the oldest and still universally used technique, is in many respects and for many products the cheapest process because of its suitability for short runs.compression moulding is similar to injection moulding in the respect that it also utilizes heat and pressure. However, the application of heat and pressure are quite different.
DESCRIPTION OF COMPRESSION MOULDS(HYDRAULIC PRESS)
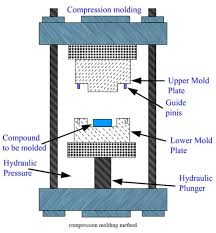
The mould has two halves, each carrying a portion of the cavity. At first, the uncured raw material, known as the charge, is pre-heated and placed in the lower half. The mould sections are also heated beforehand.Once the operator is content with the material’s placement, the plug (the movable half of the mould), lowers down into the fixed mould. Due to the pressure from the plug, the charge takes the mould cavity shape. The mould applied heat to cure the rubber in its new shape. Finally, the moulded rubber comes out as the final product.
A typical cycle of this consist of the following sequence of operations.
(1) Open mould
(2) Eject moulded part or parts
(3) Clean the mould surface with air blast
(4) Lood inserts or removable mould section ( required)
(5) Close mould,low pressure, fast travel,high pressure,and final close
(6) If necessary, breathe mould before final close
(7) Hold mould closed under pressure for cure time duration.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF HYDRAULIC MOULDS
The hydraulic moulds are mainly classified in to three types.
- Flash type moulds
- Positive type moulds
- Semi type moulds
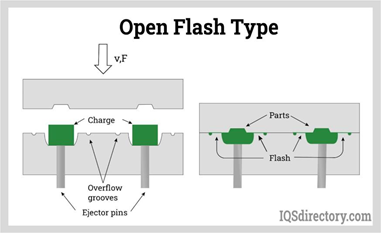
FLASH TYPE MOULDS
This type of mould is not suitable for deep draw parts, because the moulding pressure exerted is not sufficient to move the plastic material flow any great distance. The material flowing across the land area has no other restrictions to its movement. This characterize the name ‘flash mould’only flat and shallow parts should be moulded in a flash type mould.
The flash is always horizontal. If the mould is closed too slowly, a heavy flash will result. If the mould is closed too quickly the density of the moulded part will be and the strength impaired.
The advantages of flash type moulds are: -
(1) Lower mould costs
(2) Good for small parts
(3) Ease of loading inserts
(4) Specially dedicate inserts will not be damaged
(5) Experimental mould may be mode for prototype parts.
POSITIVE TYPE MOULD
A Positive type mould is better than flash type. This type of mould fully confine the moulding material and full mould pressure is exerted at all times. There is insufficient clearance between the cavity and the plunger for the moulding material to escape. The full pressure is exerted on the mould part. The travel of the force or plunger is limited only by the amount of plastic moulding powder placed in the die cavity. No external pressure pads or stop blocks are used to limit the closed height of the mould. The moulding must be weighed or measured accurately. Since there is little chance for escape of excess moulding material. The clearance escape between plunger and cavity, sometime called the vertical flash ring is 0.002 to0.005 in preside. The positive type mould is always most desirable where the plastic part must be very done. It is also used for moulding high impact thermosetting plastic material.
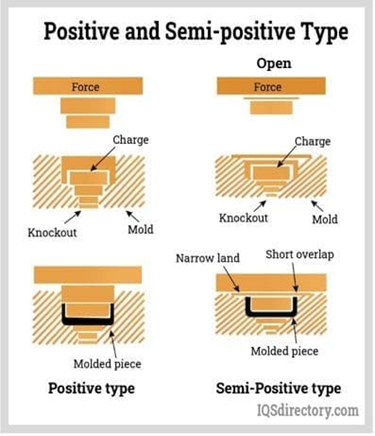
SEMI POSITIVE TYPE MOULD
Semi positive type compression moulds differ from positive moulds, because the force or plunger only telescope the body of the mould enough to exert positive pressure at the final closing of the mould. This mould construction, effective pressure on the material is assured during the last of the closing cycle, because of the short distance of vertical positive fit between the force and cavity. A slow uniform closing will allow the material to fuse completely before the mould is closed and will increase the effective pressure on the compound upon closing the press, positive pressure will be exerted, generally varies from 0.037 to 0.125, depending on the size and the shape of the part. This type of mould construction is best suited for quality production moulding.
ADVANTAGES OF COMPRESSION MOULDING
Compression moulding has several benefits/advantages. These advantages include:
- Low-cost operation
- Good surface finish
- Faster than some methods
- Flexible design
- High product uniformity
- Good dimensional accuracy
- No residual stress
- Minimizes wastage
- Extra features to consider like boss attachments, insert, etc.
However, some demerits can be associated with compression moulding. These include:
- The product's geometry is limited to enable ejection while ensuring the reuse of the mould. For example, the product cannot have undercuts.
- A product with the shape of a bottle cannot be viably produced using compression moulding, chiefly because of ejection and mould reuse concerns.
- It gives a high carbon footprint and energy consumption challenges.
- The energy consumption is typically lower than injection moulding but higher than the rest of the moulding processes.
Overall, the merits/advantages of compression moulding outweigh the demerits.
ACPL MOULDED PRODUCTS:
- Anti Vibration Pads ( Any size and colour according to the customer requirement)
- Grip for MH
- Tension Plug Pulley
- Water Proof Seal
- Rubber mat and its compounds
- Scooter mat
- Tile Mat/ Industrial Floor mat
- Bushes
- Rubber Hump/ Speed Breaker
- Floor Wipe- Rubber Bottom
- Diaphram
- Plunger Packing
- Anti Vibration Pads (Any size and colour according to the customer requirement)
- NRV (NON RETURNING VALVE

- Grip for MH

- Tension Plug Pulley

- Rubber mat and its compounds
- Scooter mat
- Tile Mat/ Industrial Floor mat

- Diaphragm

- Plunger Packing

Reference
1)Freakley. P. K. Rubber processing and production organization
2)Sommer, J. Elastomer moulding Technology
Quick Enquiry
To know more about Associated Chemicals feel free to send a message
 Our Sister Concerns
Our Sister Concerns 


Usefull Links
Get In Touch
Assochem Chambers, Bypass, Edapally,
Kochi-682024, Kerala, India.
Phones : +91 9495999349, +91 9388610189, +91 484 2339190, +91 484 2348028
E-mail : nsn@assochem.in, marketing@assochem.in, mail@assochem.in
Support

















